Welcome to the historic city of Timbuktu, a legendary trade center that played a crucial role in connecting the trans-Saharan trade routes and establishing strong trade connections with Morocco. Situated in present-day Mali, Timbuktu thrived as a bustling hub of commerce, attracting merchants from far and wide. Its strategic location in the heart of West Africa made it a pivotal point for trade caravans traveling across the Sahara Desert.
Timbuktu’s prominence in the trans-Saharan trade network can be traced back to its strategic position between the Arab world and Sub-Saharan Africa. As camel caravans traversed the unforgiving desert, Timbuktu provided essential rest stops and commercial exchanges along the way. The city became a melting pot of cultures, languages, and goods, facilitating the flow of valuable commodities between west and north Africa.
One of Timbuktu’s most significant trade connections was with Morocco. Trade caravans from Timbuktu journeyed across vast stretches of desert to reach Moroccan cities such as Marrakech and Fez. In return, Timbuktu received goods like textiles, spices, and precious metals that were highly sought after in West Africa.
As a dynamic trade center, Timbuktu attracted merchants from across Africa and the world. Its markets hummed with activity as traders bartered for salt, gold, ivory, and other commodities. The economic prosperity brought by trade transformed Timbuktu into a vibrant city, fueling advancements in arts, architecture, and scholarship.
Today, Timbuktu’s legacy as a trade hub is seen in its rich collection of manuscripts, showcasing not only the commercial exchanges but also the intellectual pursuits that thrived in the city. These manuscripts shed light on diverse subjects such as science, mathematics, history, and religion, attesting to Timbuktu’s role as a center of knowledge and learning.
Key Takeaways:
- Timbuktu was a crucial trade hub, connecting the trans-Saharan trade routes and facilitating commerce with Morocco.
- The city’s strategic location and welcoming caravanserais made it an essential stop for trade caravans crossing the Sahara Desert.
- Trade between Timbuktu and Morocco involved the exchange of textiles, spices, and precious metals.
- Timbuktu’s thriving markets and economic prosperity fueled advancements in arts, architecture, and scholarship.
- The city’s rich collection of manuscripts showcases its intellectual legacy and contributions to various fields of study.
The Importance of Timbuktu in Trans-Saharan Trade
Timbuktu, located in present-day Mali, played a pivotal role in the trans-Saharan trade network during the medieval period. Its strategic geographic location made it a vital hub for the exchange of goods between North Africa, West Africa, and Europe. Timbuktu’s significance in trans-Saharan trade can be attributed to several factors.
Firstly, Timbuktu was situated at the crossroads of major trade routes, allowing merchants to converge and conduct business. Its position between the Saharan desert and the Niger River enabled the flow of goods to and from vast regions. Merchants from Morocco, Ghana, Egypt, and other parts of Africa would travel to Timbuktu to engage in trade.
The city’s reputation as a center for learning and commerce further enhanced its importance in trans-Saharan trade. Timbuktu not only served as a marketplace for goods but also as a hub for the exchange of knowledge and ideas. Scholars and intellectuals flocked to Timbuktu, attracted by its renowned libraries and universities.
“Timbuktu served as a bridge connecting different cultures, religions, and trading partners. It was a melting pot of ideas and commerce, contributing to the wealth and development of the region.” – Dr. Amadou Keita, Historian
Timbuktu was known for the diverse range of products traded within its bustling markets. Salt from the Sahara, gold from the Sahel region, textiles, ivory, and slaves were some of the commodities exchanged. Timbuktu’s location made it an ideal trading center for goods originating from both North Africa and sub-Saharan Africa.
The city’s importance in trans-Saharan trade extended beyond its role as a marketplace. It also served as a meeting point for caravans traveling across the desert. Caravanserais, or trade inns, provided essential amenities and shelter for merchants and their animals during their arduous journeys. These caravanserais played a crucial role in facilitating trade and fostering cultural exchange.
Major Goods Traded in Timbuktu
| Commodity | Source | Destination |
|---|---|---|
| Salt | Sahara Desert | West Africa, Europe |
| Gold | Sahel Region | North Africa, Europe |
| Textiles | North Africa, Europe | West Africa |
| Ivory | Central and East Africa | North Africa, Europe |
| Slaves | Sub-Saharan Africa | North Africa, Middle East |
Timbuktu’s central role in trans-Saharan trade contributed to its economic prosperity and cultural vibrancy. The wealth generated through trade enabled the city to flourish, with magnificent mosques, libraries, and palaces built as a testament to its grandeur. Timbuktu became a symbol of prestige and attracted merchants, scholars, and travelers from far and wide.
In the subsequent sections, we will explore the specific trade connections between Timbuktu and Morocco, the trade routes that traversed the Sahara Desert, and the lasting legacy of Timbuktu’s trade activities.

Timbuktu’s Trade Connections with Morocco
In the rich history of Timbuktu as a trade hub, its connections with Morocco played a significant role in shaping commerce and cultural exchange. The trade routes between Timbuktu and Morocco facilitated the movement of goods, ideas, and people, fostering economic growth and influencing the development of both regions.
The Trans-Saharan Trade Network
The trans-Saharan trade network served as the conduit through which trade flowed between Timbuktu and Morocco. Caravans carrying precious commodities traversed the vast Sahara Desert, overcoming harsh conditions and formidable challenges to reach their destinations. These trade routes linked Timbuktu’s bustling markets with Moroccan cities such as Marrakesh and Fez.
“The trade connections between Timbuktu and Morocco were vital in advancing commercial activities and cultural exchange along the trans-Saharan routes.” – Dr. Amina Diallo, Historian
Commodities Exchanged
The trade between Timbuktu and Morocco involved the exchange of a wide range of commodities that were highly valued in both regions. Table [insert Table name here] showcases some of the key commodities traded between Timbuktu and Morocco:
| Commodity | Timbuktu’s Exports to Morocco | Morocco’s Exports to Timbuktu |
|---|---|---|
| Gold | ✓ | ✓ |
| Salt | ✓ | ✓ |
| Textiles | ✓ | ✓ |
| Spices | ✓ | ✓ |
This vibrant trade between Timbuktu and Morocco not only enriched the economies of both regions but also forged cultural connections and spurred intellectual exchange. The commodities traded were not just goods, but also catalysts for the cross-pollination of ideas and the spread of knowledge.
Impact on Morocco’s Economy
The trade with Timbuktu played a crucial role in fomenting Morocco’s economic prosperity. The influx of gold, salt, textiles, and other commodities from Timbuktu fueled Morocco’s markets, contributing to the growth of its cities and the emergence of thriving trade centers.
Legacy of Timbuktu’s Trade Connections
The trade connections between Timbuktu and Morocco left an indelible legacy on the history and culture of both regions. The cultural exchange fostered through trade shaped the arts, architecture, and even language. Moreover, the trade routes laid the foundation for later trade networks and influenced the development of commerce in West Africa and beyond.
Timbuktu as a Thriving Trade Center
Timbuktu, located in the heart of West Africa, emerged as a bustling trade center during the height of the trans-Saharan trade network. It became a hub for merchants from across Africa and beyond, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures.
The city’s strategic location, situated at the crossroads of major trade routes, contributed to its success as a trade center. Caravans loaded with valuable commodities, such as salt, gold, and textiles, flocked to Timbuktu, attracting merchants eager to take part in lucrative transactions.
The markets of Timbuktu were vibrant and diverse, with a wide array of goods available for trade. Local artisans showcased their craftsmanship, offering intricately woven textiles, exquisite jewelry, and other unique products that captured the imagination of traders.
The trade in Timbuktu brought immense economic prosperity to the region. The city flourished, with bustling streets, grand architecture, and a thriving economy that extended beyond trade. Wealthy merchants built magnificent mansions and sponsored art and scholarship, contributing to the city’s cultural and intellectual vibrancy.
“Timbuktu was a melting pot of commerce, where people from different regions and cultures converged to engage in trade. It was truly a testament to the power of trade in fostering connections and driving economic growth.” – Local historian
The trade activities in Timbuktu attracted merchants from far and wide. Arabic, Berber, and African traders established networks, forging bonds that transcended cultural and linguistic barriers. This cultural exchange enriched the city and left a lasting legacy on its architecture, language, and traditions.
To accommodate the influx of traders, Timbuktu had numerous caravanserais, which served as trading posts and resting places for merchants. These caravanserais provided essential services such as accommodations, storage facilities, and security, ensuring a smooth and efficient trade experience for all.
Merchants and their Journeys
The merchants who ventured to Timbuktu were not just driven by profit but also by a quest for knowledge. They brought with them valuable manuscripts, scientific works, and religious texts, transforming Timbuktu into a center of learning and scholarship.
The lively trade scene in Timbuktu attracted traders from across the Sahara Desert and beyond. Berber and Tuareg traders ventured south from Morocco, bringing salt, textiles, and other commodities. On the other hand, African traders from the Ghana and Mali Empires brought gold, ivory, and agricultural products for exchange.
The successful trade in Timbuktu brought prosperity to the region, creating a flourishing economy that supported the growth of arts, education, and architecture. The city’s magnificent mosques, libraries, and universities bear witness to its rich history as a trade center and intellectual hub.

Popular Trade Goods in Timbuktu
| Commodity | Description |
|---|---|
| Salt | Essential for preservation, seasoning, and trade |
| Gold | A highly prized commodity coveted by traders |
| Textiles | Exquisitely woven fabrics showcasing local craftsmanship |
| Manuscripts | Valuable literary and scientific works gathered from across the world |
| Ivory | A luxury item used for carvings and ornaments |
| Agricultural Products | Fresh produce and grains from the fertile lands of the region |
The trade center of Timbuktu thrived for centuries, attracting traders from distant lands and fostering the exchange of goods, ideas, and knowledge. Its economic prosperity and cultural richness continue to captivate historians, archaeologists, and visitors alike, making Timbuktu a living testament to the power of trade in shaping civilizations.
Trade Products in Timbuktu
In Timbuktu, a vibrant and bustling trade hub, various products were traded, making it a center for commerce and cultural exchange. The city’s strategic location along the trans-Saharan trade routes facilitated the exchange of diverse goods. Let’s explore some of the trade products that were prominent in this historic city:
Salt
Timbuktu was known for its salt trade, with caravans bringing salt from the desert to be traded in the city. This essential commodity was highly valued and played a crucial role in the economies of Timbuktu and the surrounding regions.
Gold
As a major center for trade, Timbuktu was also renowned for its gold market. Gold was sourced from the Mali Empire and exchanged for various goods, attracting merchants from distant lands.
Textiles
Timbuktu was celebrated for its intricate textiles, including vibrant fabrics, garments, and tapestries. Skilled weavers produced these textiles using traditional techniques, creating sought-after products that were in high demand.
Manuscripts
Another unique aspect of Timbuktu’s trade was the exchange of manuscripts. The city became known for its rich collection of ancient manuscripts, which covered various subjects such as science, philosophy, and Islamic teachings.
Other Valuable Commodities
In addition to salt, gold, textiles, and manuscripts, Timbuktu traded a host of other valuable commodities. These included ivory, spices, leather goods, agricultural products, and much more.
The trade products in Timbuktu were a testament to the city’s economic prosperity and its role as a vibrant center for commerce and cultural exchange. The city’s location and the goods exchanged contributed to its status as a significant trade hub along the trans-Saharan and Morocco routes.
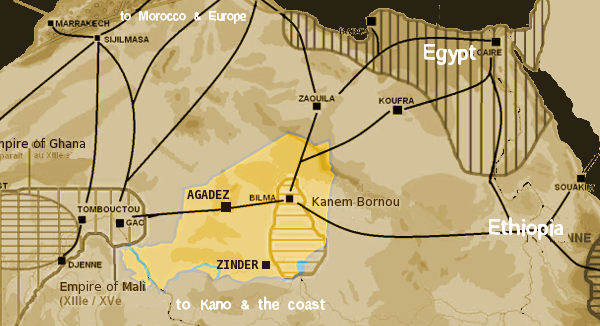
Trans-Saharan Trade Routes
In addition to its importance as a trade hub, Timbuktu played a crucial role in connecting various regions through the extensive network of trans-Saharan trade routes. These routes served as the lifelines for commercial exchanges, fostering cultural and economic interactions across the vast Sahara Desert.
Let’s explore some of the major trans-Saharan trade routes that intersected in Timbuktu:
Salt Route: Tindouf to Timbuktu
The Salt Route was a prominent trade route that connected Tindouf, a salt-producing region in present-day Algeria, to Timbuktu. Salt, a valuable commodity essential for preserving food, was transported by caravans across the arid Saharan landscape.
Gold Route: Bambuk to Timbuktu
The Gold Route linked Bambuk, a renowned gold-producing region in present-day Mali, with Timbuktu. This route facilitated the trade of luxurious gold products, attracting merchants from afar and fueling the wealth of both Timbuktu and the trans-Saharan trade routes network.
Textile Route: Egypt to Timbuktu
The Textile Route connected Timbuktu with Egypt and the Middle East, enabling the exchange of exquisite textiles and fabrics. Timbuktu’s position as a trade center allowed it to serve as a junction between different trade routes, expanding its influence and cultural footprint.
These are just a few examples of the trans-Saharan trade routes that converged in Timbuktu. The city’s strategic location at the edge of the Sahara Desert made it a vital crossroads for merchants and traders, facilitating the flow of goods, ideas, and knowledge across vast distances.
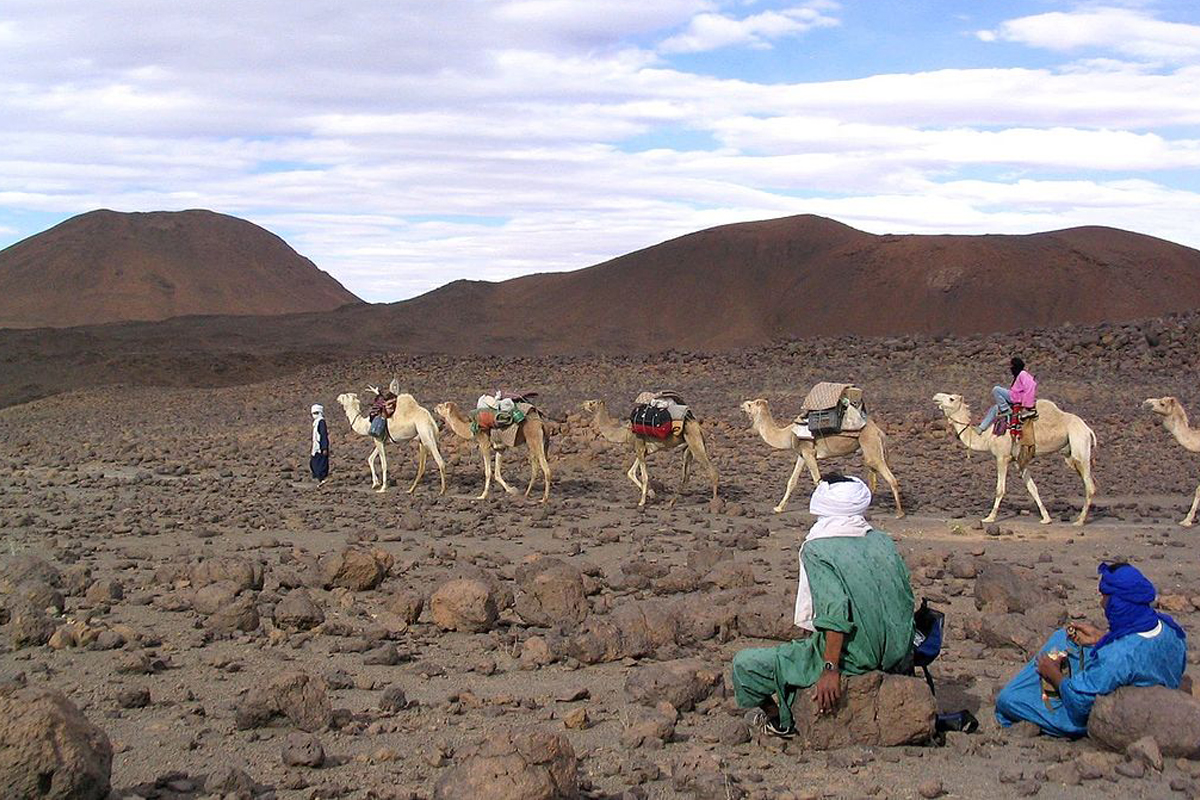
Caravans and Trade Caravanserais
In the bustling world of trans-Saharan trade, caravans and trade caravanserais played a pivotal role in facilitating the exchange of goods and ideas between Timbuktu and other destinations along the trade routes. These caravan networks were vital for the success and prosperity of Timbuktu as a trade hub.
Caravans, consisting of a group of merchants and their accompanying pack animals, traversed the vast expanse of the Sahara Desert, navigating treacherous terrain and unpredictable weather conditions. Loaded with valuable goods such as salt, gold, textiles, and manuscripts, these caravans were the lifeline of trade, connecting Timbuktu to other African regions and beyond.
“The caravans were the arteries through which wealth, knowledge, and culture flowed from one corner of Africa to another,” says Dr. Fatima Diallo, an expert in African trade history.
To support the caravans and ensure their successful journey, trade caravanserais were strategically established along the trans-Saharan routes. These caravanserais, also known as resting places, provided essential services and facilities for the weary travelers, serving as trading hubs, accommodations, and storage facilities.
The trade caravanserais offered a safe haven for merchants and their caravan members, offering protection from bandits and nomadic tribes. Moreover, these rest stops provided the opportunity for merchants to interact, exchange goods, and negotiate deals, fostering a vibrant and dynamic trade ecosystem.
Due to the long and arduous journeys, these caravanserais were strategically located at regular intervals, ensuring that caravans had access to essential resources such as water, fodder, and provisions. The trade caravanserais played a crucial role in sustaining the trade networks that connected Timbuktu with Morocco, Egypt, Spain, and other distant lands.
The Importance of Caravans and Trade Caravanserais
| Benefits | Importance |
|---|---|
| Safe Passage | Protected merchants and their valuable cargo from bandits and nomadic tribes. |
| Trade Opportunities | Allowed merchants to interact, exchange goods, and negotiate deals in a vibrant trade ecosystem. |
| Rest and Resupply | Provided a safe haven for caravans to rest, replenish supplies, and prepare for the next leg of their journey. |
| Connectivity | Created a network of interconnected trade routes, facilitating trade between Timbuktu and distant lands. |
The caravans and trade caravanserais were the backbone of trans-Saharan trade, ensuring the smooth flow of goods, knowledge, and culture. Without these crucial elements, Timbuktu’s trade prominence and the exchanges with Morocco and other destinations would not have been possible.
The Wealth and Legacy of Timbuktu Trade
Timbuktu’s trade activities brought a wealth of prosperity to the city and left an enduring legacy that extends beyond economic contributions. The wealth generated by Timbuktu’s trade hub fueled the growth of the city and fostered cultural, intellectual, and architectural advancements.
Cultural Contributions
The trade routes that converged in Timbuktu facilitated the exchange of ideas, knowledge, and artistic expressions. As a result, the city became a cultural melting pot, attracting scholars, poets, and artists from across Africa and the Islamic world. The vibrant trade scene in Timbuktu nurtured a rich tapestry of diverse cultures, languages, and traditions.
Intellectual Advancements
Timbuktu emerged as a renowned center of learning, attracting scholars and students who sought to study the Quran, law, and various disciplines of Islamic sciences. The wealth generated through trade supported the establishment of numerous Quranic schools and libraries, leading to the accumulation of a vast collection of manuscripts.
“Timbuktu was synonymous with education, attracting scholars from all over Africa, who came to learn and exchange knowledge.”
Architectural Marvels
The prosperity brought by trade also influenced the city’s architecture. Timbuktu boasts remarkable architectural gems, such as the Djinguereber Mosque, the Sankore Mosque, and the Sidi Yahya Mosque. These magnificent structures stand as testaments to the thriving trade. And the architectural expertise of the artisans who contributed to their construction.
Legacy for Future Generations
The legacy of Timbuktu’s trade continues to inspire scholars, historians, and archaeologists. The manuscripts found in Timbuktu’s libraries shed light on various subjects, including medicine, astronomy, mathematics, and literature, providing valuable insights into the intellectual achievements of past civilizations. These manuscripts are preserved and studied to ensure that the legacy of Timbuktu’s trade endures for future generations.
Timbuktu Manuscripts: A Testament to Trade and Knowledge
The city of Timbuktu, renowned for its role as a trade hub, is not just a testament to commercial exchange but also a treasure trove of knowledge. The rich collection of Timbuktu manuscripts discovered in recent years showcases the intersection of trade and intellectual pursuits in this vibrant city.
The Timbuktu manuscripts, dating back to the 13th century, are a testament to the depth and breadth of knowledge that thrived in the region. These manuscripts cover a wide range of subjects, including religion, science, medicine, literature, law, and more. They were written by scholars and intellectuals who sought to preserve and share their expertise with others.
The manuscripts offer valuable insights into the intellectual and cultural climate of Timbuktu during its heyday as a trade center. They reveal the city’s role as a center for learning, attracting scholars from across the African continent and beyond. These scholars engaged in vibrant intellectual debates and produced works that advanced knowledge in various fields.
One of the notable aspects of the Timbuktu manuscripts is their diversity. The collection includes works written in Arabic, Fulfulde, Songhay, and other local languages, illustrating the linguistic and cultural richness of the region. These manuscripts were traded alongside other commodities, further emphasizing the close connection between trade and intellectual endeavors in Timbuktu.
“The Timbuktu manuscripts represent a bridge between the commercial and intellectual realms, showcasing the integral role played by trade in the exchange of ideas and knowledge.”
Thanks to various preservation efforts, numerous Timbuktu manuscripts have been digitized and made accessible to researchers and the public. This has enabled scholars from around the world to study and appreciate the profound contributions made by ancient African civilizations.
The Timbuktu manuscripts stand as a testament to the intellectual prowess and cultural vibrancy that once thrived in this trade center. They serve as a reminder of the importance of preserving and celebrating the diverse heritage of Africa and its significant contributions to human knowledge.
| Key insights from the Timbuktu manuscripts: |
|---|
| 1. The manuscripts cover a wide range of subjects, including religion, science, medicine, literature, and law. |
| 2. They were written by scholars and intellectuals from Timbuktu and other parts of Africa. |
| 3. The manuscripts emphasize the connection between trade and intellectual pursuits in Timbuktu. |
| 4. They provide valuable insights into the intellectual and cultural climate of Timbuktu during its trade heyday. |
| 5. Preservation efforts have allowed for the digitization and accessibility of the Timbuktu manuscripts. |

Decline of Timbuktu Trade
The once-thriving trade in Timbuktu eventually saw a decline due to various factors. Shifts in trade routes and political instability in the region played a significant role in the waning prominence of Timbuktu as a trade hub.
“Over time, the decline of Timbuktu’s trade became evident as trade routes shifted and political turmoil took hold,” explains Dr. Fatima Diallo, a historian specializing in the region.
“The trade routes that once flowed through Timbuktu began to divert to other cities and ports, as new coastal trading routes emerged. This change in trade patterns had a direct impact on Timbuktu’s trade activities and economic prosperity,” says Dr. Diallo.
Additionally, the political instability in the region, marked by conflicts and invasions, hindered smooth trade operations in Timbuktu. The disruption caused by these events led to a decline in commercial activities and a loss of confidence among traders.
“The political instability created an atmosphere of uncertainty, making traders reluctant to invest in Timbuktu. This further contributed to the decline of trade in the region,” adds Dr. Diallo.
Impact on Local Economy
The decline of Timbuktu’s trade had a profound impact on the local economy. The reduction in trade activities significantly affected livelihoods and economic growth in the region.
“Timbuktu, once known for its bustling markets and vibrant trade, experienced an economic downturn as trade declined. This resulted in a decrease in revenue and opportunities for local traders and businesses,” notes Professor Aminata Sow, an economist studying regional trade.
Repercussions on Cultural Exchange
The decline of Timbuktu’s trade also had suggestion for cultural exchange. The city’s trade activities had facilitated the flow of goods, ideas, and knowledge between various regions.
“With the decline of trade, the exchange of ideas and goods diminished, impacting cultural diversity and intellectual growth,” says Dr. Mamadou Diop, a cultural anthropologist.
This decline highlighted the interconnected nature of trade and cultural exchange in sustaining the vibrancy and richness of Timbuktu’s heritage.
Preservation and Rediscovery
Despite the decline in trade, efforts are underway to preserve and rediscover the trade history of Timbuktu. Various organizations and institutions, including UNESCO, support initiatives aimed at reviving Timbuktu’s trade heritage.
| Preservation Efforts | Rediscovery Projects |
|---|---|
| Conservation of historic trade routes and buildings | Archaeological excavations to uncover remnants of past trade |
| Restoration of trade caravanserais for cultural tourism | Digitization and preservation of Timbuktu manuscripts |
| Promotion of trade-related festivals and events | Research and documentation of forgotten trade practices |
These preservation and rediscovery efforts aim to not only safeguard Timbuktu’s trade heritage but also promote its historical significance to a global audience.
Revitalization and Preservation Efforts
Efforts to revitalize the trade heritage of Timbuktu and preserve its historic sites have been underway, driven by the recognition of the city’s cultural significance and the need to safeguard its rich history for future generations. Recognizing the importance of Timbuktu as a UNESCO World Heritage site, various initiatives have been implemented to ensure the revitalization and preservation of this ancient trade hub.
One significant preservation effort is the conservation of the many historic manuscripts that have survived in Timbuktu. These manuscripts are a testament to the intellectual and cultural exchange that took place alongside the vibrant trade activities in the city. To protect these valuable documents, which cover a wide range of topics including science, religion, and literature, organizations like the Timbuktu Manuscripts Project have been working tirelessly to digitize and preserve these priceless artifacts.
Furthermore, restoration projects have focused on the physical infrastructure of Timbuktu, including its traditional mud-brick buildings and architectural landmarks. The aim is to restore and maintain the city’s unique architectural heritage, showcasing the intricate craftsmanship and design that characterized Timbuktu during its golden age as a trade center.
Timbuktu’s revitalization and preservation efforts are crucial not only for the city but also for understanding the broader history of trans-Saharan trade and the cultural exchange it facilitated.
UNESCO’s Involvement and Conservation Programs
Recognizing the historical and cultural significance of Timbuktu, UNESCO has played a crucial role in supporting preservation efforts. The UNESCO World Heritage Committee designated Timbuktu as a World Heritage site in 1988, emphasise the need for international collaboration in protecting the city’s invaluable heritage.
In addition to the World Heritage designation, UNESCO has provided technical assistance and financial support for conservation projects in Timbuktu. This includes initiatives aimed at the preservation and restoration of mosques, mausoleums, libraries, and cultural centers, all contributing to the revitalization of Timbuktu’s trade heritage.
Local and International Collaboration
Revitalization and preservation efforts in Timbuktu have benefited from collaborations between local communities, government agencies, and international organizations. The involvement of local stakeholders is essential for ensuring the sustainability of preservation projects and fostering community pride in Timbuktu’s rich cultural heritage.
International partnerships between UNESCO, academic institutions, and cultural organizations have also played a crucial role in the restoration and preservation of Timbuktu. These collaborations have provided expertise, funding, and technical support to help conserve the city’s unique architectural wonders and promote the revitalization of its trade legacy.
Through these combined efforts, Timbuktu is gradually reemerging as a vibrant cultural and historical destination, attracting visitors eager to explore its trade heritage and witness the ongoing preservation endeavors firsthand.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Timbuktu’s historic significance as a trade hub cannot be exaggerated. It played a pivotal role in the trans-Saharan trade network, attaching West Africa with North Africa, specifically Morocco. Through strategic geographic location and growing commercial activities. Timbuktu facilitated the exchange of various goods and materials, participating to the economic prosperity of the region.
The trade connections between Timbuktu and Morocco were instrumental in fostering cultural exchange and profitale growth. Merchants moved along well-established routes, carrying goods such as salt, gold, textiles, and manuscripts. These trade networks not only stimulated commerce but also smoothed the transmission of knowledge and ideas.
Although Timbuktu’s prominence as a trade center declined over time. Efforts are underway to revitalize its trade heritage and preserve its historical sites. UNESCO’s recognition and preservation projects exhibit the commitment to safeguarding the enduring legacy of Timbuktu. And its impact on the trans-Saharan trade network.
In conclusion, Timbuktu stands as a testament to the power of trade and commerce, leaving behind a rich legacy that transcends borders. Its significance as a trade hub and its connections to Morocco continue to captivate historians, archaeologists, and researchers worldwide.
FAQ
What is the historic significance of Timbuktu?
Timbuktu holds immense historic significance as a trade hub, particularly in the trans-Saharan and Morocco routes. Its strategic location facilitated extensive trade networks and cultural exchanges between various African regions and beyond.
How did Timbuktu contribute to the trans-Saharan trade network?
Timbuktu played a crucial role in the trans-Saharan trade. It’s network by serving as a central meeting point for merchants traveling across the Sahara Desert. It facilitated the exchange of goods such as salt, gold, textiles, and manuscripts.
What were the trade connections between Timbuktu and Morocco?
Timbuktu had significant trade connections with Morocco, with various trade routes linking the two regions. Merchants transported goods like gold, salt, textiles, and manuscripts, fostering economic and cultural ties between Timbuktu and Morocco.
How did Timbuktu thrive as a trade center?
Timbuktu thrived as a trade center due to its bustling markets, skilled merchants, and the considerable wealth generated through trade. It served as a melting pot of diverse cultures and fostered economic prosperity in the region.
What were the main trade products in Timbuktu?
Timbuktu was known for its diverse range of trade products, including valuable commodities such as salt, gold, textiles, and manuscripts. These goods were exchanged within the city and across various trade routes.
What were the trans-Saharan trade routes?
The trans-Saharan trade routes were extensive networks that crisscrossed the Sahara Desert, connecting Timbuktu to other African regions. These routes facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures across vast distances.
How did caravans and trade caravanserais contribute to trade in Timbuktu?
Caravans consisting of camels and traders played a vital role in facilitating trade between Timbuktu. And destinations along the trans-Saharan routes. Trade caravanserais provided shelters and services for these caravans, serving as important trading hubs.
What was the wealth and legacy of Timbuktu’s trade?
Timbuktu’s trade activities brought immense wealth and prosperity to the region, contributing to its economic growth and cultural development. The trade legacy of Timbuktu is evident in its architectural landmarks, intellectual pursuits, and lasting cultural influence.
What are Timbuktu manuscripts, and how do they relate to trade?
Timbuktu manuscripts are a proof to the meeting of trade and knowledge in the city. These manuscripts contain valuable visions into various subjects, including commerce, Islam, and African history. Reflecting the intellectual exchange fostered by trade in Timbuktu.
What led to the decline of Timbuktu’s trade prominence?
Several factors contributed to the decline of Timbuktu’s trade importance, including shifts in trade routes, political instability in the region. And the diminishing economic importance of the trans-Saharan trade network.
What efforts are being made to revitalize and protect Timbuktu’s trade heritage?
Various revitalization and protection efforts are in progress to defence Timbuktu’s trade heritage. These include UNESCO’s recognition of its cultural significance and conservation projects aimed at preserving its historic sites and manuscripts.


